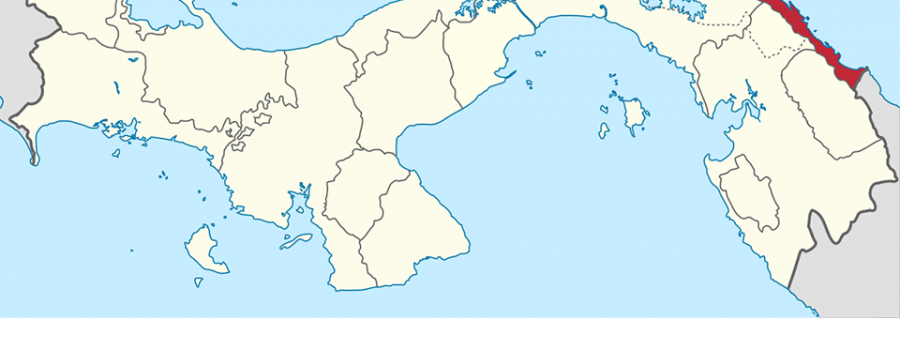
The Guna Yala Region is a semi-autonomous territory in Panama, home to the Guna people. The region enforces its own laws and regulations, while the Panamanian government actively supports health, education, and safety services.
Demography of Guna Yala
The Guna Yala Region has a population of more than 31,557, according to the 2010 census. If you’re looking for more detailed information about the Guna people, you can visit the UNICEF Panama website.
Geographical Location of Guna Yala
Located along Panama’s Caribbean coast, Guna Yala stretches 145 miles in length and varies between 6 and 12 miles in width. The mainland covers approximately 1,238 square miles. Moreover, when you include the marine areas, such as reefs and islands, the total area exceeds 2,085 square miles, with over 300 islands.
Limits of Guna Yala Region

To the north, Guna Yala borders the Caribbean Sea, while to the east, it touches Colombia. Its southern boundaries include five regions: the Embera Region, Darién Province, Wargandí, Madugandí, and Panama Province. Meanwhile, the western side meets Colón Province. For additional information, you can explore the Lonely Planet Panama page.
Know more Nusagandi Viewpoint
Protected Wilderness Area in Guna Yala
In 1994, the Guna Congress officially designated the Corregimiento de Narganá as a Protected Wilderness Area. This area spans 100,000 hectares, representing 31% of Guna Yala’s mainland territory.
Flora and Fauna in Guna Yala

The Guna Yala Region encompasses 320,600 hectares of mountainous forests and includes a vast archipelago. Its rich biodiversity makes it a key part of the Mesoamerican Biological Corridor. Furthermore, conservation efforts continue to protect its unique ecosystems.
Vegetation and Biomes in Guna Yala Region
This region is home to tropical moist forests, very humid premontane forests, and tropical forests. About 63.5% of the land consists of primary forests. Additionally, around 70% of the total area is covered by both primary and secondary forests.
Moreover, the coral reefs in Guna Yala are among the best-preserved in both the Northwest Atlantic and Central Caribbean regions. For more information, visit the Smithsonian Institution’s page on coral reefs.
Marine Ecosystems in Guna Yala Region
The marine ecosystems in Guna Yala include mangroves, extensive reef networks, and seagrass prairies. Additionally, the region’s reefs are home to 49 species of coral, making it one of the most biodiverse areas in the Caribbean.
Relief of Guna Yala Region

The topography of Guna Yala is quite diverse. Mountain ranges descend towards the Caribbean coast, with peaks such as Dianmaiayala (850 m) and Obu (747 m) standing out. These variations in terrain enhance the region’s breathtaking landscapes.
Hydrography of Guna Yala Region
Rivers in Guna Yala flow into the Caribbean Sea. There are more than 20 major rivers that provide fresh water to many Guna communities. The pristine condition of these rivers reflects the region’s strong commitment to environmental conservation.
Governmental Political Division

Politically, Guna Yala is divided into two electoral circuits. Circuit 10-1 includes 32 communities, and Circuit 10-2 encompasses 19. These circuits are represented by two deputies in Panama’s Legislative Assembly. If you’re interested in more political details, you can visit the OAS page on Panama.
Administrative and Cultural Political Division
The Guna Yala Region is divided into several sectors for administrative and cultural governance. It consists of 50 formal communities, with many located on islands. Coastal and mainland communities actively participate in the General Guna Congress as well.